Reinforcement Learning Methods in Public Health
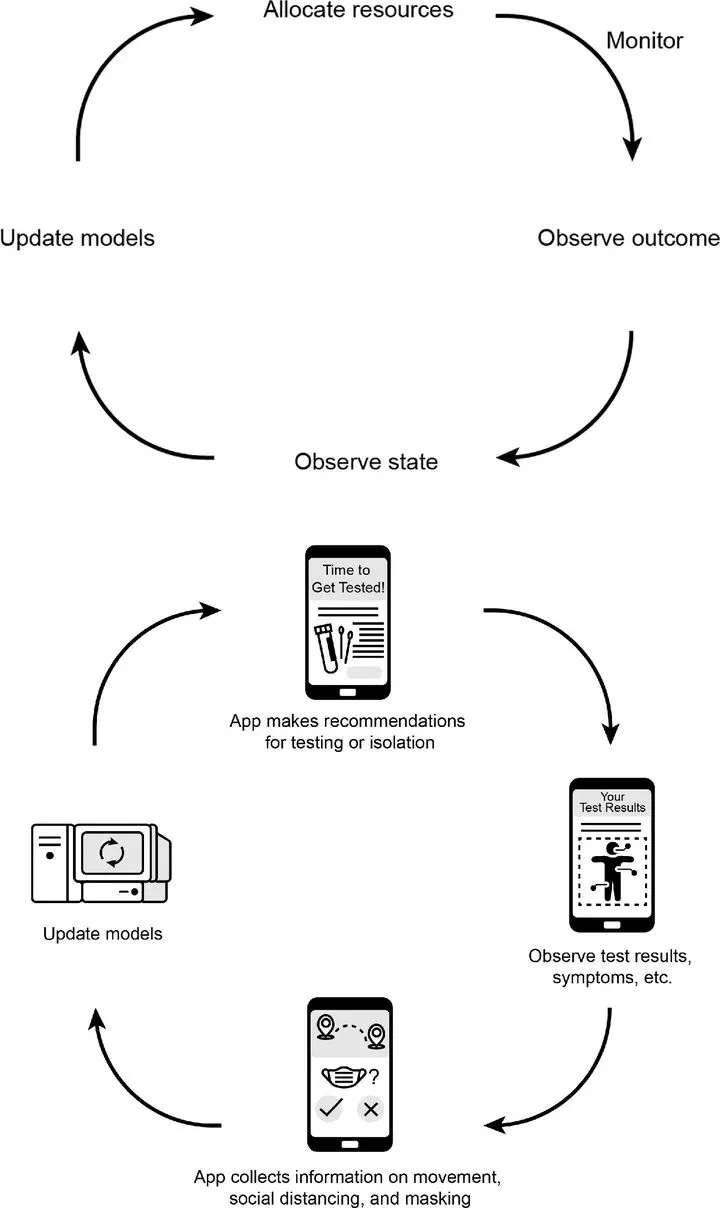 Image credit: Unsplash
Image credit: UnsplashAbstract
Reinforcement learning (RL) is the subfield of machine learning focused on optimal sequential decision making under uncertainty. An optimal RL strategy maximizes cumulative utility by experimenting only if and when the information generated by experimentation is likely to outweigh associated short-term costs. RL represents a holistic approach to decision making that evaluates the impact of every action (ie, data collection, allocation of resources, and treatment assignment) in terms of short-term and long-term utility to stakeholders. Thus, RL is an ideal model for a number of complex decision problems that arise in public health, including resource allocation in a pandemic, monitoring or testing, and adaptive sampling for hidden populations. Nevertheless, although RL has been applied successfully in a wide range of domains, including precision medicine, it has not been widely adopted in public health. The purposes of this review are to introduce key ideas in RL and to identify challenges and opportunities associated with the application of RL in public health.
Type
Publication
Clinical Therapeutics